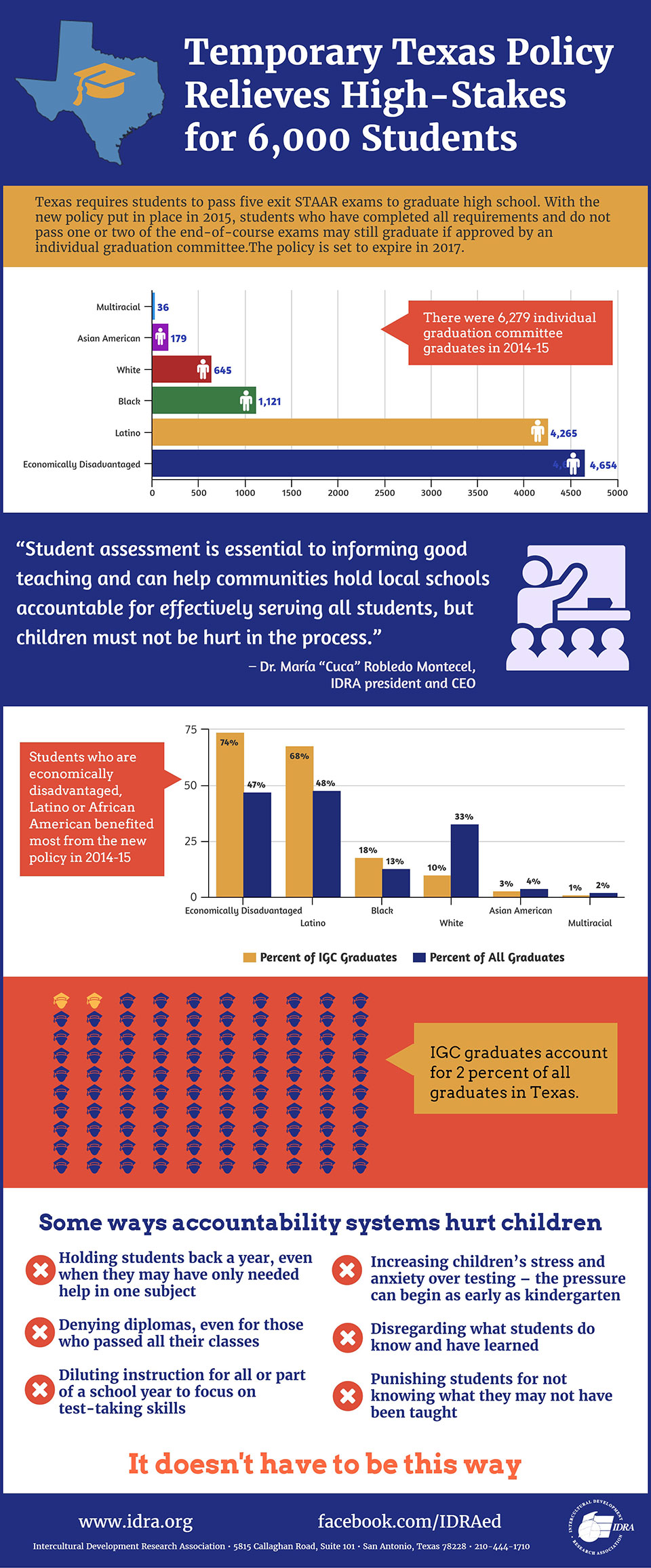
Attrition and Dropout Rates in Texas
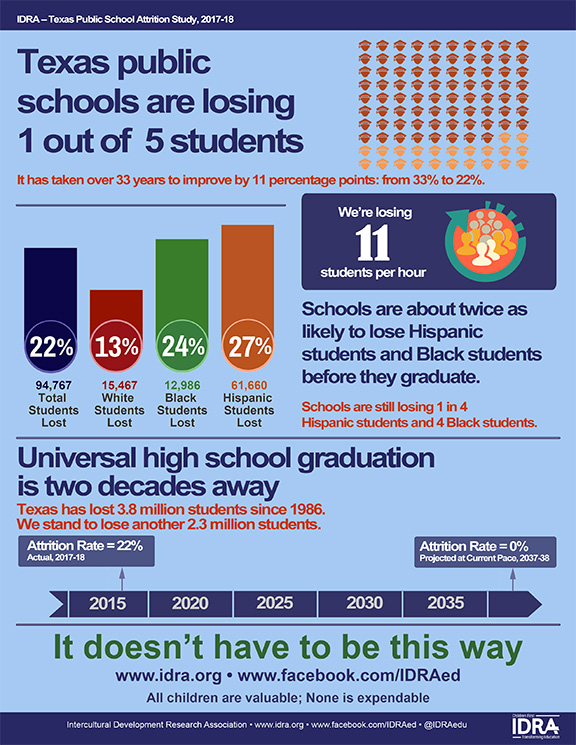
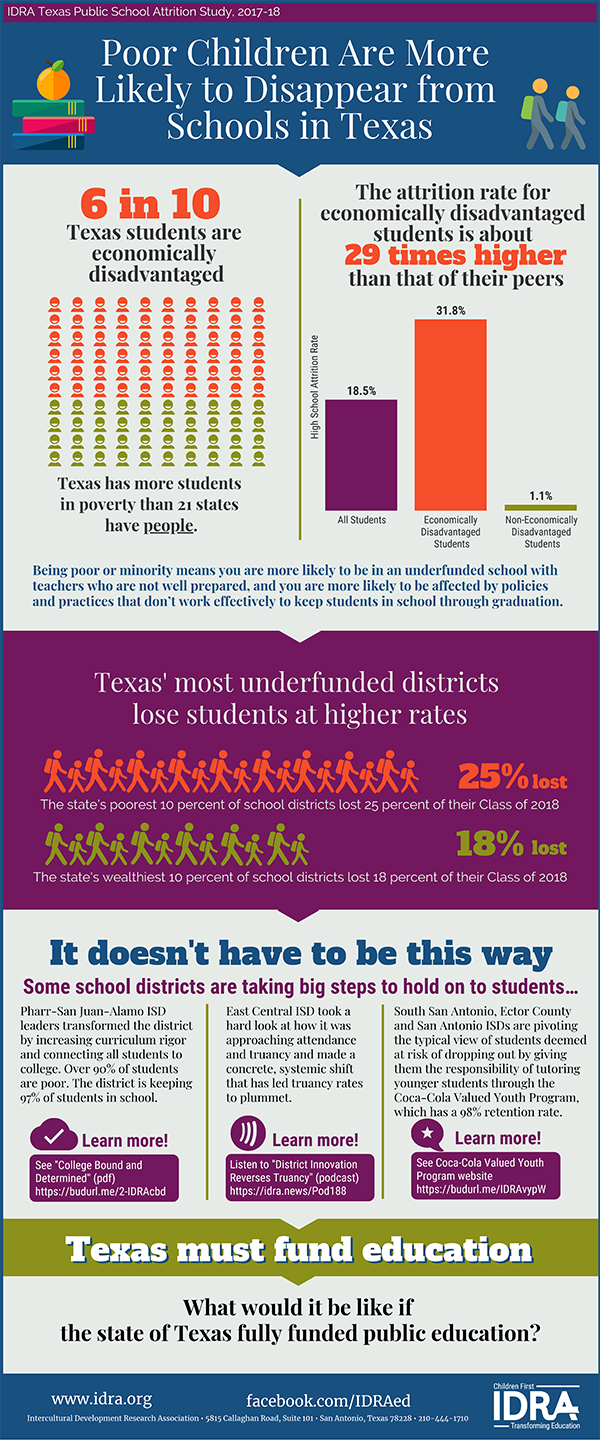
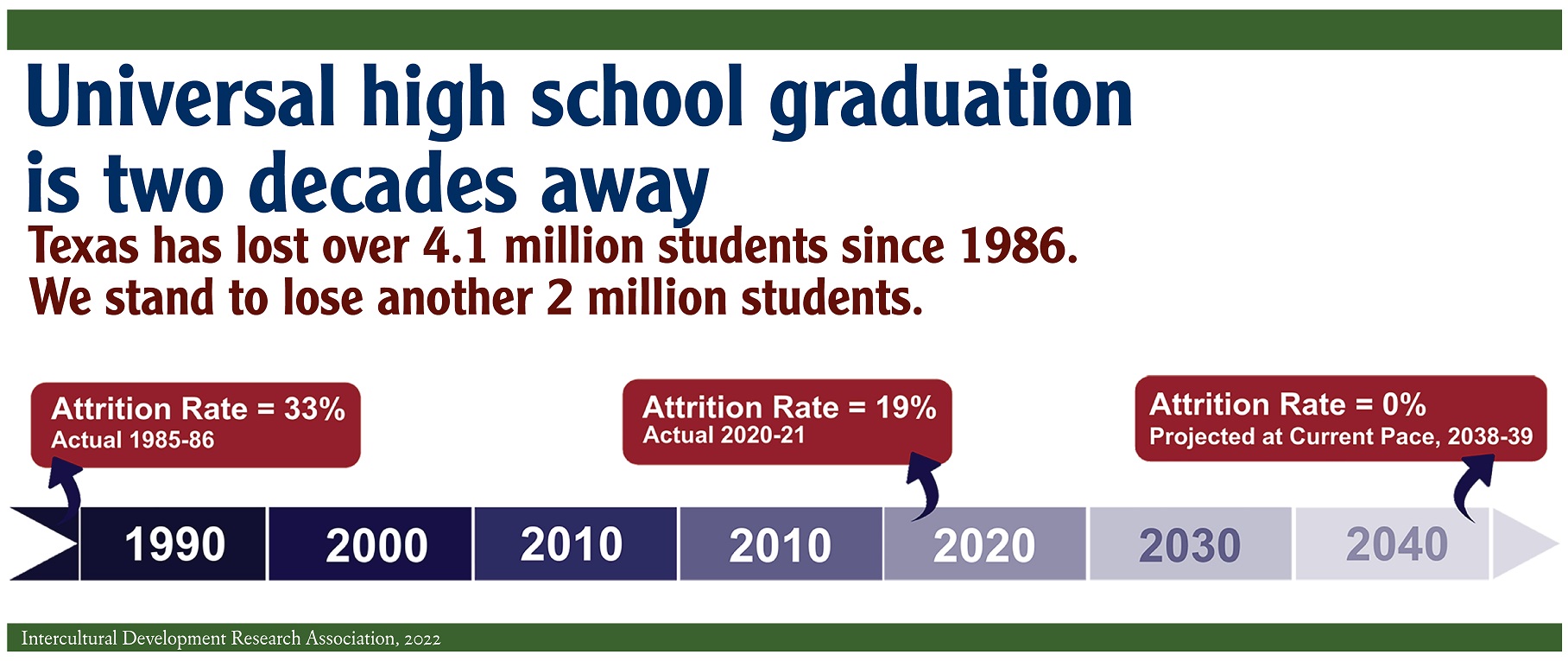
Texas public schools are losing one out of five students.
Each year, IDRA releases its attrition study. Attrition rates are an indicator of a school’s holding power, or the ability to keep students enrolled in school and learning until they graduate. Key findings from the latest study show the following.
- Texas schools are failing to graduate more than one of every five high school students
- The Texas public school attrition rates increased each year since 2020-21.
- It has taken almost four decades for Texas to reduce the state’s attrition rate by a mere 11 points from 33% to 22%.
- Total attrition rates and those of the state’s largest groups (Black, Latino, white) are higher than the year before COVID-19.
- For the class of 2023, Latino students and Black students were more than twice as likely to leave school without graduating than white students.
- The attrition rate gap between white students and Black students has more than doubled between 1985-86 and 2022-23.
See reporter FAQs and resources regarding attrition and dropout data (and downloadable graphics).
Quick Links to IDRA’s Attrition Study Stories and Resources
Attrition Study 2022-23: Texas Public School Attrition Study, 2022-23 – Pandemic-Legacy High School Attrition Rate Increases Two Points; Black-White Gap Widens to 15 Points
Article for the 2022-23 study: Schools Struggle to Hold On to Students – Preview of IDRA’s 38th Annual Texas Public School Attrition Study
Infographic: Texas public schools are losing one out of five students
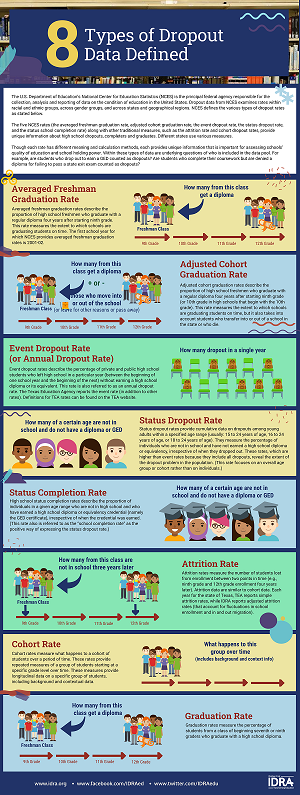
Infographic: 8 Types of Dropout Data Defined
Infographic: 6 Policies and Practices that Lead to Higher Dropout Rates
Trend graphs: See attrition rates and numbers over 10 years
Sign up for email notices
Additional Resources
Book: Courage to Connect: A Quality Schools Action Framework
Overview of the Valued Youth Partnership program, which keeps 98 percent of students in school (PDF)
Ideas and Strategies for Action

 2020-21 Attrition Study
2020-21 Attrition Study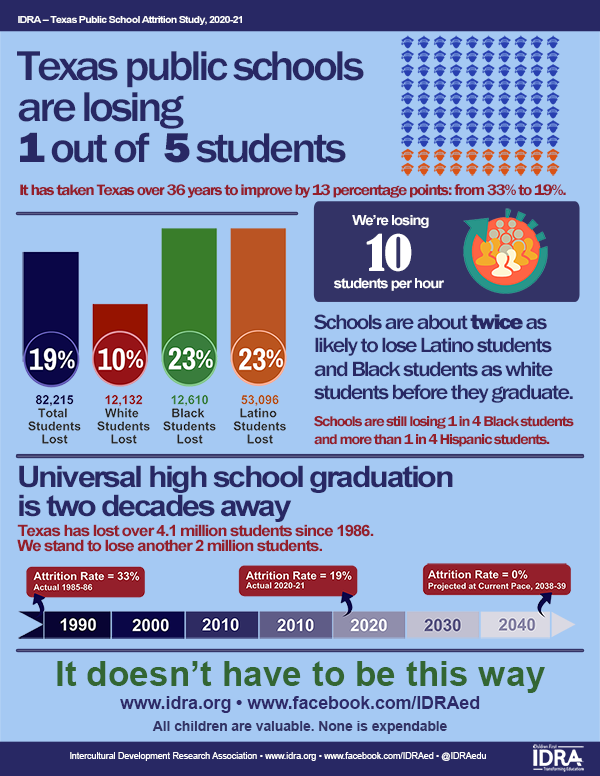 Texas public schools are losing 1 of 5 students
Texas public schools are losing 1 of 5 students